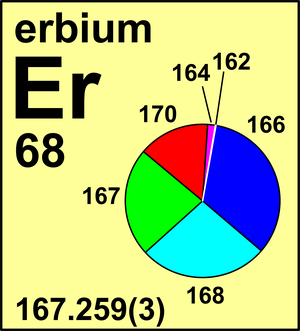
Erbium
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| 162Er | 161.928 787(6) | 0.001 39(5) |
| 164Er | 163.929 207(5) | 0.016 01(3) |
| 166Er | 165.930 299(8) | 0.335 03(36) |
| 167Er | 166.932 054(8) | 0.228 69(9) |
| 168Er | 167.932 376(8) | 0.269 78(18) |
| 170Er | 169.935 47(1) | 0.149 10(36) |
In 1969, the Commission assessed Ar(Er) = 167.26(3). The atomic weight and uncertainty of erbium were changed to their current values in 1999 as a result of new mass-spectrometric measurements. The "g" notation arises from the presence of naturally occurring fission products found in fossil reactors at Gabon, south-west Africa.
© IUPAC 2003
CIAAW
Erbium
Ar(Er) = 167.259(3) since 1999
The name derives from the Swedish town of Ytterby, where the ore gadolinite (in which it was found)
was first mined. Erbium was discovered by the Swedish surgeon and chemist Carl-Gustav Mosander in 1843
in a yttrium sample. He separated the yttrium into yttrium, a rose-coloured salt he called terbium and a
deep-yellow peroxide that he called erbium.