Gallium
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
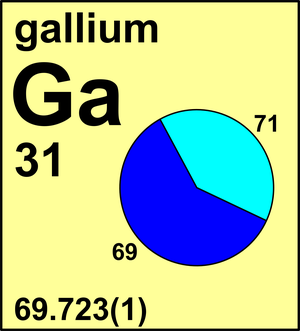
| 69Ga | 68.925 573(8) | 0.601 08(50) |
| 71Ga | 70.924 702(6) | 0.398 92(50) |
In 1961, the Commission recommended Ar(Ga) = 69.72, based on the chemical ratio determinations as well as the isotope-abundance determinations. Recalculating the chemical ratios based on current values of the other atomic weights involved yields Ar(Ga) = 69.735, while the mass-spectrometric value with current atomic masses gives Ar(Ga) = 69.72. Furthermore, highly precise coulometric assay of Ga and As yielded Ar(Ga) = 69.737. Meanwhile, new mass-spectrometric measurements confirmed the earlier mass-spectrometric values, yielding Ar(Ga) = 69.724(2). Facing with this dataset, the Commission recommended an atomic weight of Ar(Ga) = 69.723(4) in 1983 favouring the mass-spectrometric data.
Significant variations occur in the n(69Ga)/n(71Ga) ratio of commercially high-purity Ga from different lots of material and different manufacturers, some exhibiting ratios 0.19 % higher and 0.12 % lower than the laboratory reference material. Based on this information, in 1987 the Commission recommended Ar = 69.723(1), which has remained unchanged since that time.
Purification of Ga by successive recrystallizations is accompanied by small variations in isotopic composition, which measurably affect the triple-point temperature of gallium.
© IUPAC 2003
CIAAW
Gallium
Ar(Ga) = 69.723(1) since 1987
The name derives from the Latin gallia for France. It was discovered in zinc blende by the French chemist Paul-Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in
1875. It was first isolated in 1878 by Lecoq de Boisbaudran and the French chemist Émile-Clément Jungflesch.
Isotopic reference materials of gallium.