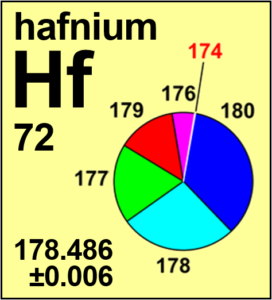
Hafnium
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| 174Hf | 173.940 05(2) | 0.001 61(2) |
| 176Hf | 175.941 41(1) | 0.0524(14) |
| 177Hf | 176.943 23(1) | 0.1858(9) |
| 178Hf | 177.943 71(1) | 0.2728(6) |
| 179Hf | 178.945 83(1) | 0.1363(3) |
| 180Hf | 179.946 56(1) | 0.3512(16) |
In 1961, the Commission recommended Ar(Hf) = 174.49 based on new mass-spectrometric determinations. In 1985, the uncertainty was re-assessed as Ar(Hf) = 174.49(2), and in 2019 the Commission recommended changes to the standard atomic weight based on recent determinations and evaluations of its isotopic composition.
The minor isotope, 174Hf, is an α-emitter with the very long half-life of 2.0(4)×1015 a. It does not affect Ar(Hf) even in a geologic time frame. However, 176Hf is the principal product of 176Lu decay, so that small but detectable variations in 176Hf abundance with geologic age and Lu association occur. These variations are overshadowed by larger uncertainties in the value for Ar(Hf), which, however, does not preclude their use in geochronology. In addition, some rare terrestrial materials can have abnormal isotopic compositions of hafnium with the most extreme known case being sedimentary chert from South Africa having atomic-weight value of 178.447.
CIAAW
Hafnium
Ar(Hf) = 178.486 ± 0.006 since 2019
The name derives from the Latin hafnia for Copenhagen. An element named celtium was erroneously
claimed to have been discovered in 1911 by the French chemist Georges Urbain in rare earth samples,
until the Danish physicist Niels Bohr, predicted hafnium's properties using his theory of electronic configuration
of the elements. Bohr argued that hafnium would not be a rare earth element, but would be
found in zirconium ore. Hafnium was discovered by the Dutch physicist Dirk Coster and the Hungarian physicist
George von Hevesy in 1923, while working at Bohr's Institute in Copenhagen.