Iron
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
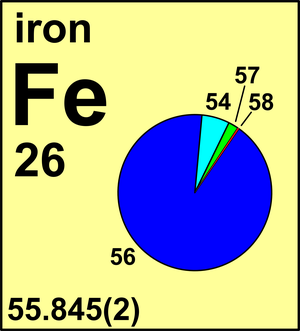
| 54Fe | 53.939 608(3) | 0.058 45(105) |
| 56Fe | 55.934 936(2) | 0.917 54(106) |
| 57Fe | 56.935 392(2) | 0.021 19(29) |
| 58Fe | 57.933 274(3) | 0.002 82(12) |
In 1961, the Commission recommended Ar(Fe) = 55.847(3) based on the average value of two reported mass-spectrometric determinations. In 1993, the Commission changed the recommended value for the standard atomic weight to Ar(Fe) = 55.845(2) based on calibrated mass-spectrometric measurements carried out on a metallic iron sample of high purity.
Several studies have indicated natural isotope fractionation in iron-containing materials. The magnitude of the uncertainty assigned to the atomic-weight value was based mainly on the reported variations of Fe isotopic composition; however, subsequent studies now indicate somewhat different ranges. According to the compilation by the Commission, reported δ56Fe values range from −2.9 ‰ with Ar(Fe) = 55.8448 in human blood to +1.36 ‰ with Ar(Fe) = 55.8453 in part of a banded iron formation. Here δ56Fe refers to n(56Fe)/n(54Fe) relative to the reference material IRMM-014.
© IUPAC 2003
CIAAW
Iron
Ar(Fe) = 55.845(2) since 1993
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon iron of unknown origin. The element has been known from
prehistoric times. The symbol Fe is derived from the Latin ferrum for "firmness". It is of interest
to note that 56Fe requires more energy to be formed than any other nuclide. It is, therefore, the ultimate endproduct
of stellar nuclear fusion.
Isotopic reference materials of iron.