Osmium
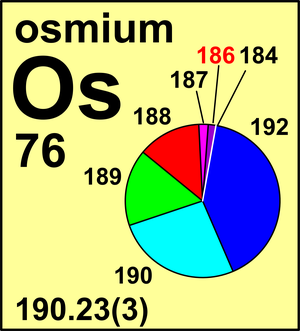
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| 184Os | 183.952 493(6) | 0.0002(2) |
| 186Os | 185.953 838(5) | 0.0159(64) |
| 187Os | 186.955 750(5) | 0.0196(17) |
| 188Os | 187.955 837(5) | 0.1324(27) |
| 189Os | 188.958 146(5) | 0.1615(23) |
| 190Os | 189.958 446(5) | 0.2626(20) |
| 192Os | 191.961 48(2) | 0.4078(32) |
In 1969, the Commission recommended Ar(Os) = 190.2(l). At this time, osmium had the largest uncertainty among all standard atomic weights, equalled with lead (for which, however, the atomic weight is affected by natural variability, not applicable to osmium). In 1991, the Commission considered new isotope measurements yielding an atomic weight having a significantly improved precision, and recommended Ar(Os) = 190.23(3).
One of the minor isotopes, 186Os, is radioactive with a very long half-life of 2.0×1015 a. It undergoes α-decay into stable 182W but does not affect Ar(Os) even over geologic time. 187Os is the stable product of β– active 187Re decay. As a result, osmium occurs with anomalous atomic weight as a trace element in Re-bearing rocks. The "g" annotation is thereby justified.
© IUPAC 2003
CIAAW
Osmium
Ar(Os) = 190.23(3) since 1991
The name derives from the Greek osme for "smell" because of the sharp odor of its volatile oxide. Both
osmium and iridium were discovered simultaneously in a crude platinum ore by the English chemist
Smithson Tennant in 1803.
Isotopic reference materials of osmium.