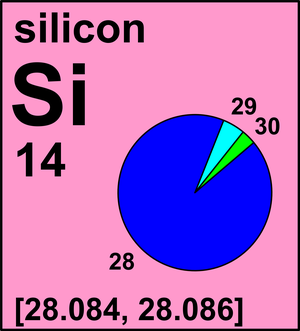
Silicon
| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| 28Si | 27.976 926 535(3) | [0.921 91, 0.923 18] |
| 29Si | 28.976 494 665(4) | [0.046 45, 0.046 99] |
| 30Si | 29.973 7701(2) | [0.030 37, 0.031 10] |
The Commission has noted that, while new values with considerably smaller uncertainties (uncertainty 0.000 12 on an atomic-weight value of 28.085 65) had been determined on Si isotopic reference materials, the range in isotopic composition of normal terrestrial materials prevent a more precise standard atomic weight being given. δ(30Si) measurements are expressed relative to NBS 28 SiO2 as distributed by IAEA and NIST. The lowest δ(30Si) value (−3.7 ‰) is reported from biogenic sponge spicules for which x(30Si) = 0.030 816 and Ar(Si) = 28.085 22. The highest δ(30Si) value (+3.4 ‰) is reported from silicified algal matter in sediments for which x(30Si) = 0.031 023 and Ar(Si) = 28.085 78.
In recent history, Ar(Si) determinations have been directly related to attempts to establish as accurately as possible the relationship between atomic unit of mass (dalton) and the macroscopic SI unit of mass (kilogram) as represented by determinations of Avogadro constant.
Radioactive 32Si is a cosmogenic isotope, and it is potentially available from the nuclear industry in sufficient quantities to make it of value in isotope dilution mass spectrometry measurements, given its relatively long half-life.
Atomic weights of the elements 2009 by M.E. Wieser and T.B. Coplen. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011 (83) 359-396
CIAAW
Silicon
Ar(Si) = [28.084, 28.086] since 2009
The name derives from the Latin silex and silicis for "flint". Amorphous silicon was discovered by the
Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1824. Crystalline silicon was first prepared by the French
chemist Henri Sainte-Claire Deville in 1854.
Natural variations of silicon isotopic composition
Isotopic reference materials of silicon.